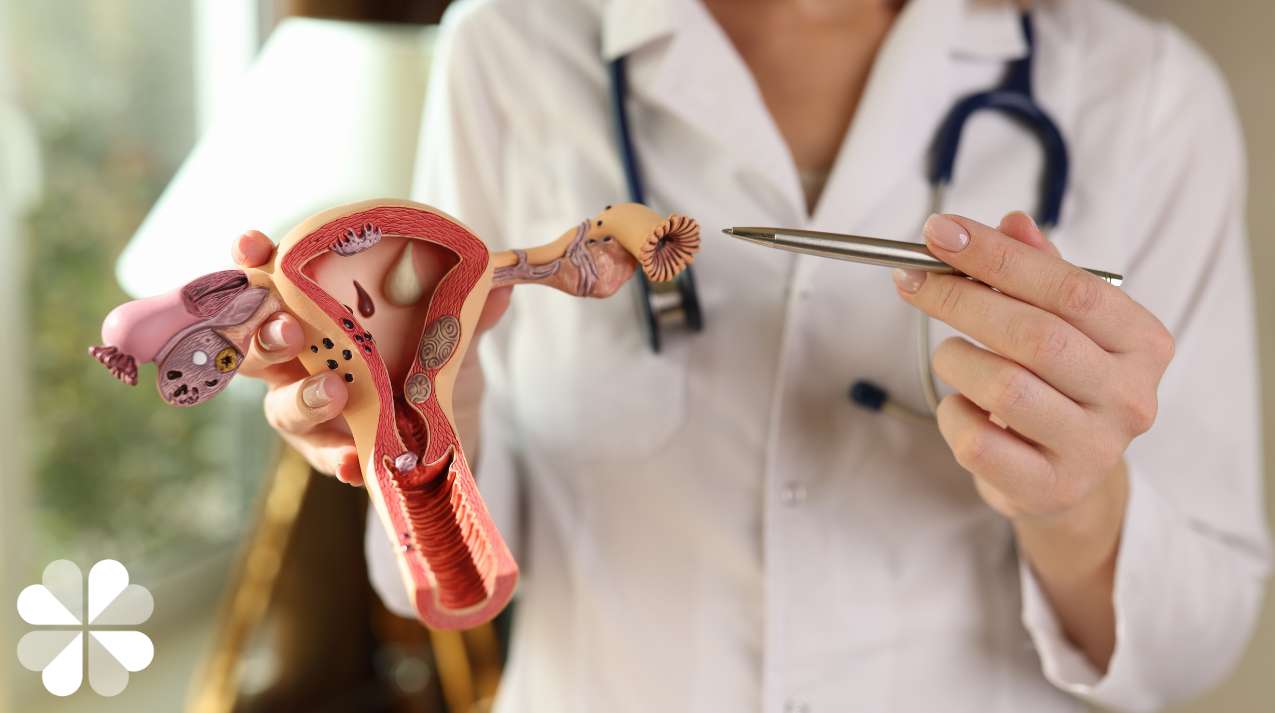
Urinary incontinence is the loss of bladder control, ranging from occasional leakage of urine to complete inability to control urination. This problem is more common in women, who are twice as likely as men to experience this condition.
If you suffer from frequent urination, loss of urine or overactive bladder, in CanaryDoctor We are here to help you. Find a doctor and schedule an appointment near you today.
Symptoms of urinary incontinence
Common symptoms of urinary incontinence include:
- Leaking urine when coughing, sneezing, laughing, or exercising.
- Sudden and uncontrollable desire to urinate.
- Frequent urination
- Waking up several times a night to urinate.
- Urinate during sleep.
Your doctor will evaluate these symptoms, examine you, and diagnose you appropriately.
Causes of urinary incontinence
Causes of urinary incontinence may include:
- Pregnancy and childbirth: The uterus presses on the bladder during pregnancy, causing incontinence. Vaginal birth can stretch and weaken the muscles that support bladder control.
- Menopause: Decreased estrogen levels during menopause thin vaginal and urethral tissue, affecting bladder control.
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs): UTIs can cause temporary incontinence.
- Medications: Some medications, such as diuretics, can cause urinary incontinence.
- Nerve damage: Diseases or injuries that affect the nerves that control the bladder can cause incontinence.
- Tumors: Tumors in the urinary tract can interfere with bladder control.
- Constipation: May put additional pressure on the bladder.
- Side effects of hysterectomy: Removal of the uterus can affect bladder control.
- Excessive consumption of diuretics: Caffeine, vitamin C and chocolate can increase urine production and aggravate incontinence.
Types of urinary incontinence
There are several types of urinary incontinence, each with different triggers and treatments:
- Stress-induced: Loss of control when sneezing, laughing, lifting heavy objects, or doing intense exercise.
- Overflow: Incomplete emptying of the bladder, causing constant “leaks” of urine.
- Urgency: Sudden and urgent need to urinate, followed by involuntary urination.
- Functional: Inability to get to the bathroom on time due to conditions such as arthritis.
- Mixed: Combination of one or more of the previous types.
Factors riesgo
Common risk factors include:
- Sex: Women are more prone due to the structure of the urinary tract and reproductive organs.
- Age: Menopause and aging reduce muscle strength and bladder capacity.
- Body weight: Being overweight puts additional pressure on the bladder.
- Smoking: Increases the risk of developing urinary incontinence.
Prevention
Although urinary incontinence cannot always be prevented, you can reduce the risk by:
- Keep a healthy weight.
- Perform Kegel exercises and other exercises to strengthen the bladder and pelvic floor.
- Avoid foods and drinks that cause incontinence, such as caffeine, chocolate, spicy and acidic foods.
- Do not smoke or quit smoking.
- Attend regular medical appointments.
- Seek treatment for urinary tract infections, constipation, and other conditions that can trigger incontinence.
Urinary incontinence can be uncomfortable and affect your quality of life. At Canary Doctor, we are here to offer you the best treatment and care. Don't wait any longer, consult with our specialists and improve your well-being today.